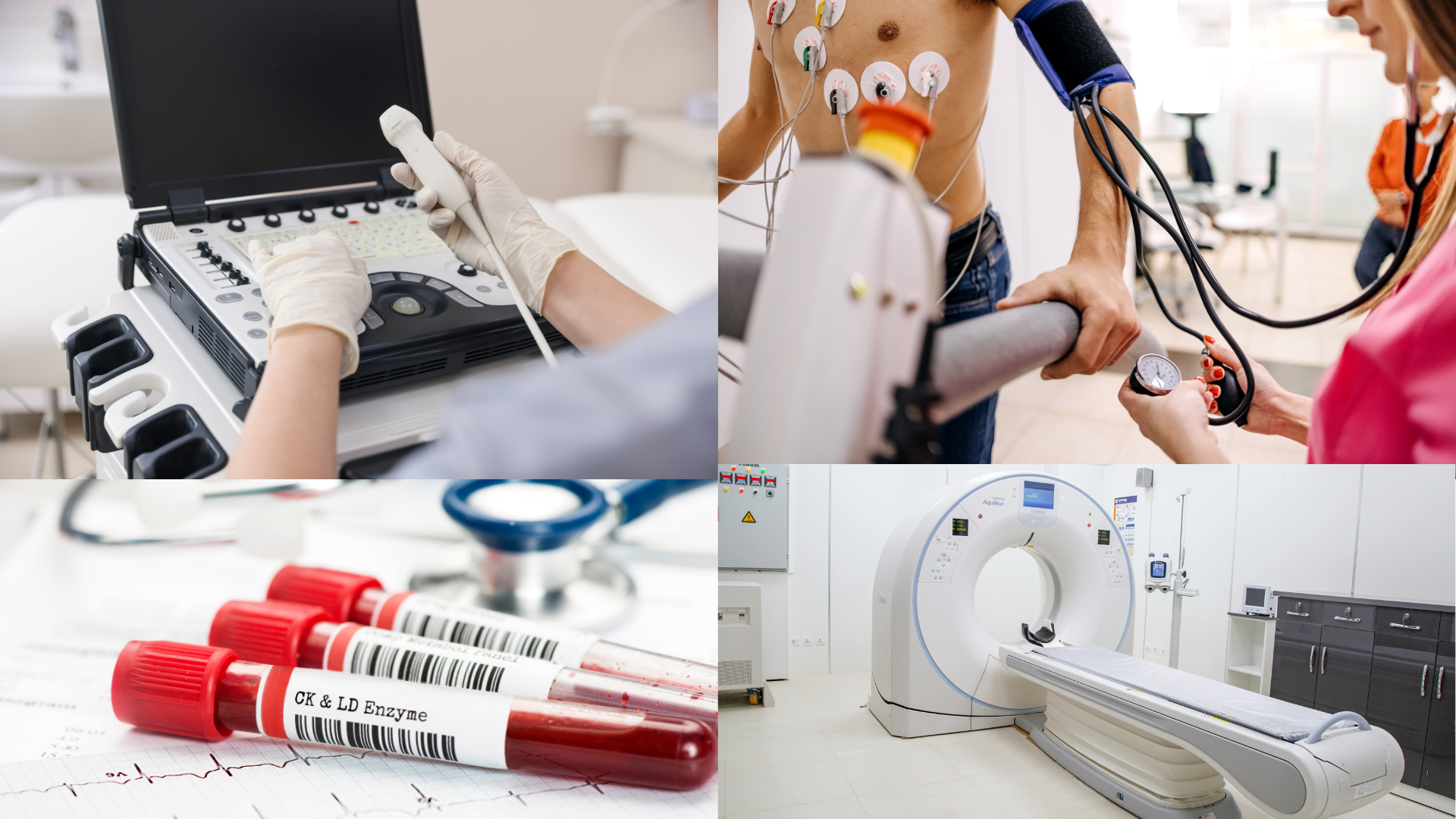
What Are the Different Cardiac Tests?
Cardiac tests are used to assess how well your heart is working and to identify problems with heart rhythm, structure, blood flow, or overall function. They play a key role in diagnosing heart conditions, guiding treatment, and monitoring long-term heart health.
Many patients ask what the different cardiac tests are and why one test might be chosen over another. In this writing, we explain the most commonly used cardiac tests, what each one shows, and when they are typically recommended.
Why Cardiac Tests Are Used
Cardiac tests help doctors understand what is happening inside the heart. Some tests look at the heart’s electrical activity, others assess blood flow or the strength of the heart muscle, and some focus on identifying narrowing in the coronary arteries.
These tests may be requested if you have symptoms such as chest pain, palpitations, breathlessness, dizziness, or fatigue. They are also used for monitoring known heart conditions or as part of preventive heart screening for people with risk factors like high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, or a family history of heart disease.
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
An ECG is one of the most common cardiac tests. It records the electrical signals that control your heartbeat. Small sensors are placed on the chest, arms, and legs, and the test takes only a few minutes. ECGs can detect irregular heart rhythms (arrhythmias), signs of strain on the heart, and evidence of previous heart damage. It is often the first test used when someone presents with palpitations or chest discomfort.
Echocardiogram (Echo)
An echocardiogram is an ultrasound scan of the heart. It shows how well the heart muscle is pumping and how the heart valves are functioning. This test is particularly useful for diagnosing heart failure, heart valve disease, cardiomyopathy, and structural abnormalities. It is painless and does not involve radiation.
Exercise Stress Test
An exercise stress test assesses how your heart performs when it is working harder. You are asked to walk on a treadmill or cycle while your heart rhythm, blood pressure, and symptoms are monitored. This test helps identify problems with blood flow to the heart that may not be present at rest. It is often used when investigating chest pain or assessing exercise tolerance.
CT Coronary Angiogram
A CT coronary angiogram is a detailed scan that looks specifically at the coronary arteries, which supply blood to the heart muscle. It can detect narrowing or blockages caused by plaque build-up. This test is particularly useful for diagnosing or ruling out coronary artery disease and is commonly used when someone has chest pain but unclear findings on other tests. For a clear explanation of CT scans, the NHS CT scan guide is a helpful resource.
Heart Rhythm Monitoring
Some heart rhythm problems occur intermittently and may not show up on a short ECG. In these cases, longer-term monitoring is used. A 24-hour or 7-day ECG monitor is a small wearable device that records your heart rhythm while you go about your normal daily activities. This helps link symptoms such as palpitations or dizziness with changes in heart rhythm. This type of monitoring is commonly used to diagnose conditions such as atrial fibrillation or other arrhythmias.
Blood Pressure Monitoring
High blood pressure is a major risk factor for heart disease. 24-hour blood pressure monitoring provides a more accurate picture than a single reading taken in clinic. The monitor records your blood pressure at regular intervals throughout the day and night, helping identify patterns and confirm whether treatment is needed.
Blood Tests
Blood tests are an important part of cardiac assessment. They can measure cholesterol levels, blood sugar, kidney function, and markers of heart strain or damage. These tests also help identify conditions such as anaemia or thyroid problems, which can affect heart function and rhythm.
Cardiac MRI
A cardiac MRI uses magnetic fields to create highly detailed images of the heart muscle and surrounding structures. It is often used when more information is needed after an echocardiogram or CT scan. This test can assess inflammation, scarring, and complex heart muscle conditions in great detail.
How Your Cardiologist Chooses the Right Test
Not everyone needs every test. The choice of cardiac test depends on your symptoms, medical history, risk factors, and initial examination findings. Often, one test leads to another if more detail is required. At WKCP, we take time to explain why a particular test is recommended and what information it will provide. Understanding the purpose of each test helps reduce anxiety and ensures you feel informed throughout the process.
What Happens After Cardiac Testing
Once your tests are complete, the results are reviewed and explained clearly. If everything is normal, you may simply receive reassurance and advice on maintaining good heart health. If a problem is identified, your cardiologist will discuss the next steps. This may include lifestyle changes, medication, further tests, or ongoing monitoring. You can contact us to discuss cardiac testing or arrange an assessment. Alternatively you can call us on 01892 526726 to book an appointment.
Quick Summary
Cardiac tests are essential tools for understanding heart health. From simple ECGs to advanced imaging, each test provides valuable insight into how the heart is functioning and whether treatment is needed. If you are experiencing symptoms or want a clearer picture of your heart health, cardiac testing can provide reassurance, early diagnosis, and guidance for long-term care.

